Helping doctors diagnose and guide your care with precision.
EEG at the Doctor’s Office
What is an EEG?
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a safe, painless test that records the electrical activity of your brain. Small sensors, called electrodes, are gently placed on your scalp using a special adhesive or cap. These sensors pick up tiny electrical signals produced by your brain cells and send them to a computer, where they are displayed as wavy lines.
Why is an EEG Done?
Doctors often recommend an EEG to help diagnose or monitor conditions such as epilepsy, seizures, sleep disorders, head injuries, or unexplained episodes of confusion. It can also be used to evaluate brain activity after a stroke or during certain treatments. The test does not involve any electricity being sent into your body; it only records what your brain is naturally producing.

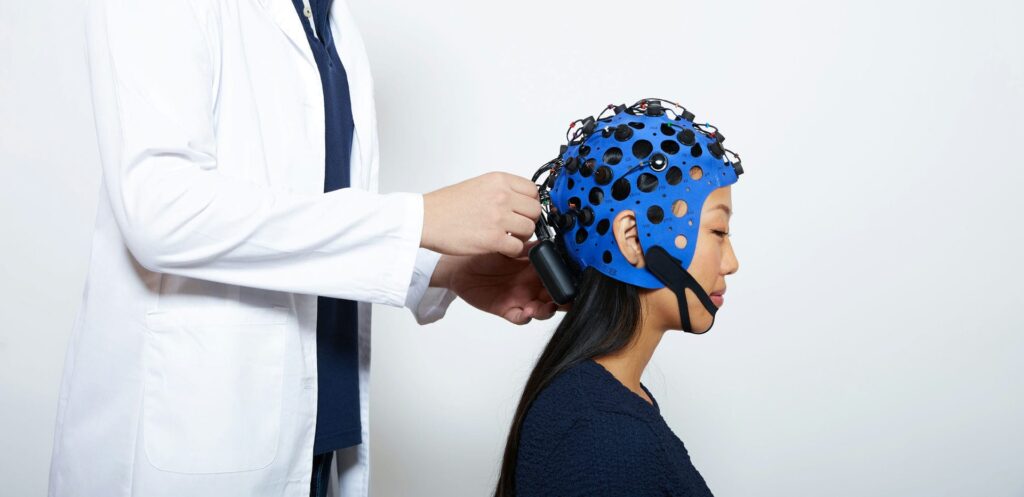
What Happens During the Test?
During the procedure, you may be asked to sit quietly, close your eyes, or perform simple tasks like breathing deeply or looking at flashing lights. These activities can help reveal patterns in your brain’s activity. The test usually takes between 30 minutes and an hour, depending on what your doctor is looking for.
After the EEG
Once the test is complete, the electrodes are removed, and you can return to your normal routine right away. There are no side effects, and the test is completely non‑invasive. Your doctor will review the results and discuss what they mean for your health.
The Importance of EEG
An EEG at the doctor’s office is an important tool that provides valuable insight into how your brain is functioning. By capturing this information, your healthcare provider can make more accurate diagnoses and tailor treatments to your specific needs. It’s a simple step that can play a big role in understanding and protecting your neurological health.